Biologic treatments have changed the way conditions like inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are managed, offering relief for many people who once struggled with constant symptoms. Yet, as with any advanced therapy, they can come with side effects that vary in type and intensity. Understanding these effects helps both patients and healthcare professionals make informed choices and respond early to any concerns.
Entyvio (vedolizumab) is a gut-selective monoclonal antibody approved for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Because it acts mainly in the digestive tract rather than throughout the body, it is often considered to have a more favorable safety profile than some other biologic medications. Even so, side effects can occur and should be carefully monitored during treatment.
This article explains the possible side effects of Entyvio, how often they appear, and what can be done to manage them safely and effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Entyvio (vedolizumab) is a gut-selective biologic approved for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, offering a targeted treatment approach.
- Most Entyvio side effects are mild and temporary, including headache, fatigue, and nasal congestion.
- Infusion reactions can occur but are usually manageable with medical supervision and proper infusion protocols.
- Rare but serious risks include PML, liver injury, and severe infections, requiring ongoing safety monitoring.
- Regular liver tests, neurological checks, and follow-ups are essential for safe, long-term management.
About: Doctor Medica is your trusted supplier of top-quality dermal fillers, viscosupplements, and more for your medical practice. We offer genuine products from leading brands at the lowest prices in the market. If you’re looking to order Entyvio online for your practice, contact Doctor Medica today.
Common and Mild Adverse Events Associated with Entyvio

Most Entyvio side effects are mild to moderate and often improve naturally as the body adjusts to treatment. These effects appear early in therapy or during clinical studies. Because Entyvio (vedolizumab) works by selectively blocking gut-specific lymphocyte migration, it limits widespread immune suppression. This gut-selective action is linked to a favorable safety profile regarding certain systemic opportunistic infections compared with non-gut-selective biologics such as TNF-alpha antagonists or natalizumab.
Common mild side effects include:
- Headache: Among the most frequent complaints, usually mild and short-lived after infusions.
- Fatigue: A temporary feeling of tiredness that improves with rest and proper hydration.
- Joint pain (arthralgia): May appear intermittently and fluctuate between treatment cycles.
- Nasal congestion or sore throat: Sometimes related to mild upper respiratory infections.
- Nausea or abdominal discomfort: Often reflects the digestive tract’s adjustment to treatment.
These symptoms rarely require stopping therapy, but patients should still inform their healthcare provider if discomfort persists or worsens. General supportive care is considered helpful for patient guidance, though it is not specific to Entyvio. Regular follow-ups allow clinicians to monitor progress, track any new effects, and maintain patient comfort throughout therapy.
Infusion-Related and Hypersensitivity Reactions with Entyvio
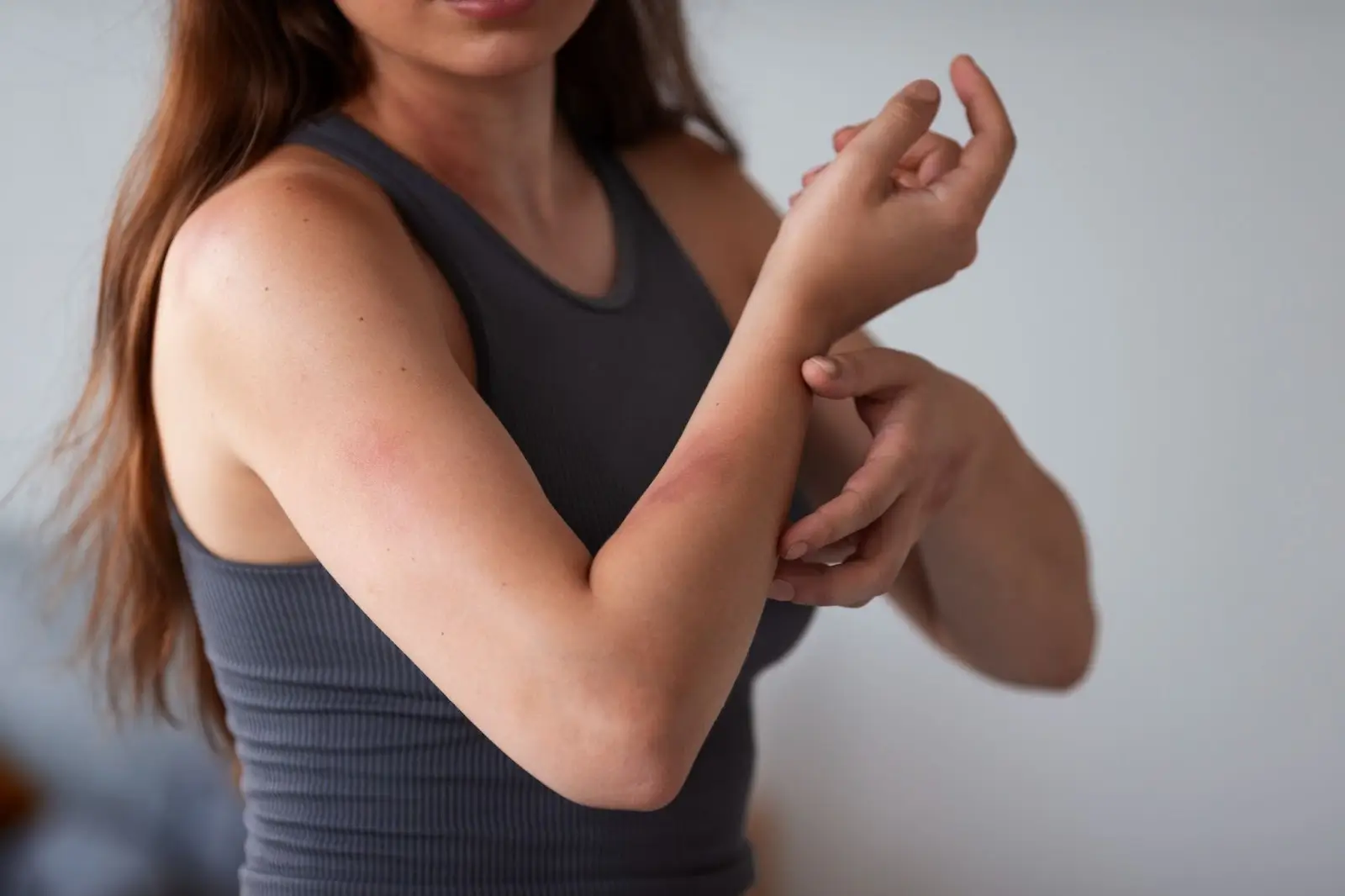
Because Entyvio is given as an intravenous infusion, some patients may experience infusion-related or hypersensitivity reactions. These generally occur during or shortly after administration, most often in the early sessions. While reactions are usually mild, medical supervision during infusions helps ensure prompt management.
Here are some of the expected reactions during this stage of the treatment:
- Flushing or warmth during infusion
- Itching or mild rash
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fever or chills within 24 hours
- Shortness of breath or chest discomfort (less common but important to report)
In rare cases, severe allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis can occur. Medical teams should have emergency medications on hand and observe patients for at least 30 minutes post-infusion. If moderate reactions appear, the infusion rate may be slowed or temporarily stopped.
Proper staff training and patient education play a key role in preventing anxiety and ensuring safety. Clear communication about infusion protocols helps patients new to biologic therapy feel more confident and secure throughout their treatment.
Rare but Serious Risks (e.g., PML, Liver Injury) of Entyvio
Though rare, some side effects require immediate medical attention. One of the most critical concerns is progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), a rare and potentially fatal brain infection caused by the JC virus. While no PML cases were reported during clinical trials, a confirmed case has occurred in the post-marketing setting in a patient with multiple contributing factors. Ongoing surveillance remains essential because of Entyvio’s immune-modulating effects.
Other severe risks may include:
- Liver injury or elevated liver enzymes: May present as jaundice, dark urine, or upper right abdominal pain. Routine liver function tests help detect early warning signs.
- Severe infections: Although Entyvio targets the gut, reduced immune activity in the gastrointestinal tract can still increase susceptibility to localized infections.
- Severe allergic reactions: Rare but potentially life-threatening, requiring immediate discontinuation and emergency medical care.
Patients should contact their healthcare provider right away if they experience vision changes, confusion, yellowing of the skin, or unexplained fever. With early detection and appropriate medical follow-up, the likelihood of lasting complications remains very low.
Risk Mitigation, Monitoring, and Management Strategies for Entyvio
Patient safety during Entyvio therapy depends on structured monitoring and management throughout treatment. The Entyvio FDA labeling highlights the importance of these strategies to maintain tolerability and long-term safety.
Safety Monitoring Strategies
- Baseline Screening: Check for tuberculosis and hepatitis before starting therapy.
- Liver Function Testing: Conduct periodic assessments to detect enzyme elevations.
- Neurological Evaluation: Watch for early signs of PML, such as confusion, imbalance, or memory loss.
- Observation During Infusions: Identify hypersensitivity reactions as they occur.
- Ongoing Follow-up: Track emerging or persistent side effects and adjust care plans as needed.
Effective communication between clinicians and patients encourages timely reporting and supports safe, consistent treatment outcomes. Early recognition of concerning symptoms allows for dose adjustment, temporary interruption, or treatment discontinuation if necessary. This proactive approach protects patient health while maintaining the benefits of therapy for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Conclusion
Clinically, Entyvio remains one of the most targeted and well-tolerated biologic options for treating conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Its gut-selective mechanism reduces systemic immune effects, allowing most patients to continue therapy safely under medical supervision.
While rare cases of liver enzyme elevation, infusion reactions, or PML highlight the need for vigilance, the overall benefit-to-risk ratio remains favorable. Safety monitoring, ongoing communication, and adherence to infusion protocols are key to maintaining this balance.
With proper medical oversight, Entyvio can help patients achieve long-term remission and improved quality of life without compromising immune function. For comprehensive safety information and updates, healthcare professionals should consult the official FDA database.
FAQs
1. What are the most common Entyvio side effects?
The most common include headache, fatigue, joint pain, and mild upper respiratory infections. These are usually temporary and improve as treatment continues.
2. How serious is the risk of PML with Entyvio?
While no cases were reported during clinical trials, a confirmed post-marketing case has been documented in a patient with multiple risk factors. Ongoing neurological monitoring remains critical as a precautionary measure.
3. Can Entyvio cause liver problems?
Yes. Rare cases of elevated liver enzymes and hepatic injury have been reported. Routine liver testing helps detect and manage potential problems early.
4. What should I do if I experience an infusion reaction?
Inform your healthcare provider immediately. Mild reactions may be managed with antihistamines or a slower infusion rate, while severe reactions require urgent medical care.
References
Kopylov U, Seidman E. Predicting durable response or resistance to antitumor necrosis factor therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2016;9(4):513-526. doi:10.1177/1756283X16638833
Ben-Horin S, Kopylov U, Chowers Y. Optimizing anti-TNF treatments in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(1):24-30. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2013.06.002
Related Articles
Joanna Carr
Radiesse vs Juvederm – Comparing Dermal Fillers
Radiesse and Juvederm use different materials to smooth wrinkles. Read more on Doctor Medica.
Joanna Carr
Botox For Bladder: Treatment, Effects, And Results
Have an interest in learning about Effects And Results Of Botox Application For Bladder? Browse Doctor Medica's extensive archive of blog postings.
Joanna Carr
Mounjaro vs Semaglutide – How Do They Compare for Weight Loss?
Compare Mounjaro vs semaglutide for weight loss, including clinical outcomes, mechanisms of action, and patient suitability.


