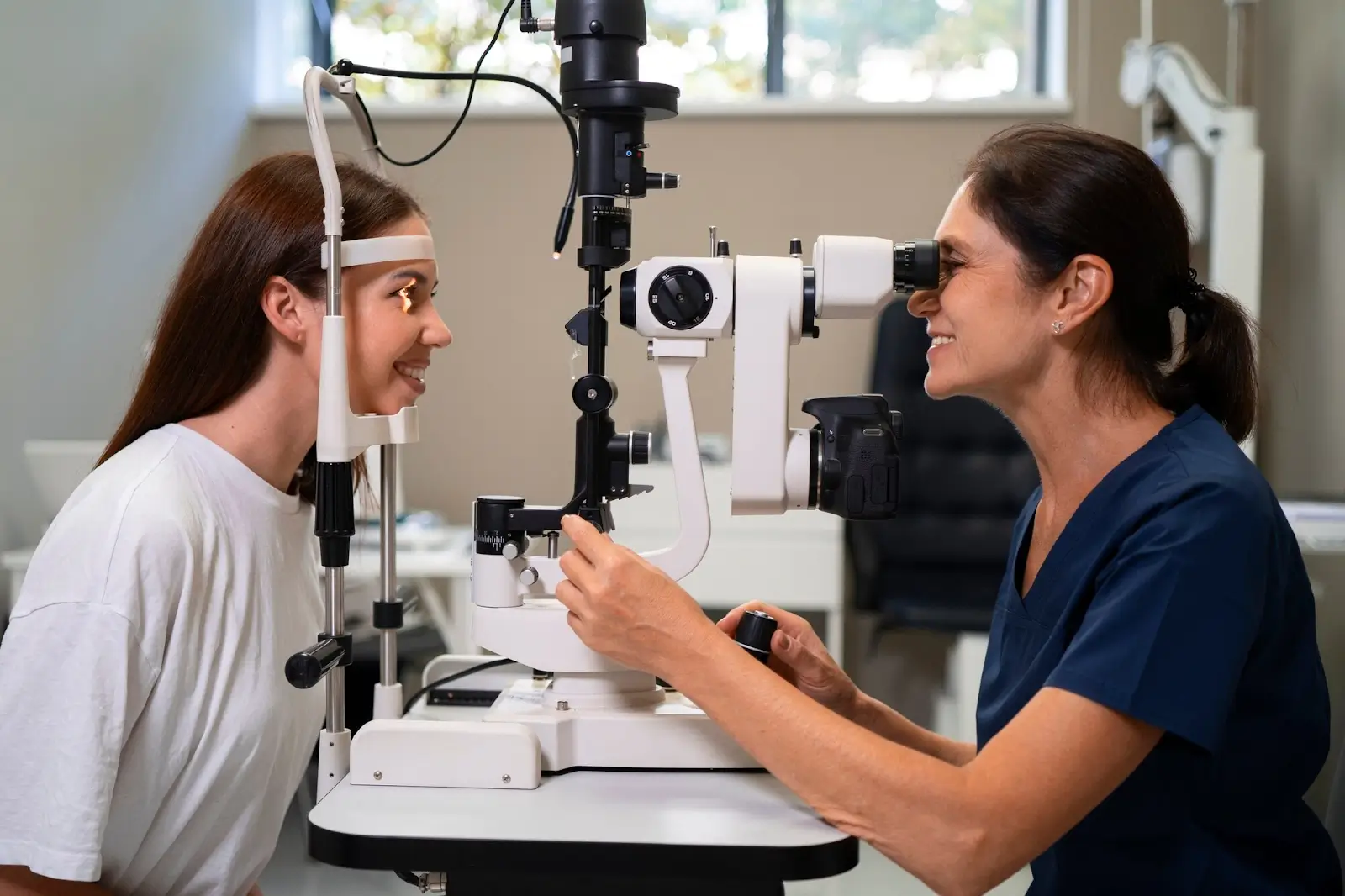
Getting the dosing right for intravitreal injections can make all the difference in preserving vision and improving quality of life—especially when managing chronic eye conditions. For patients with diseases like wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) or diabetic macular edema (DME), a consistent treatment schedule isn’t just helpful—it’s essential.
Eylea (aflibercept) is one of the most trusted medications in this space, praised for its ability to slow disease progression and reduce retinal swelling. But to get the most out of Eylea, both timing and technique matter. Sticking to the recommended dosing schedule and using precise injection methods are key to achieving safe, long-term results.
In this article, we’ll talk about the recommended Eylea dosing schedule, share best practices for injection techniques, and highlight the critical steps clinicians can take to maximize efficacy while ensuring patient safety.
Key Takeaways
- Eylea (aflibercept) requires a precise dosing schedule tailored to specific conditions like AMD, DME, DR, and RVO.
- The standard regimen typically starts with monthly injections, followed by extended maintenance intervals.
- Proper injection techniques—including sterile preparation and anatomical accuracy—are essential to avoid complications.
- Common side effects include mild eye irritation and floaters, while rare risks include retinal detachment and infection.
- Patient education improves adherence; understanding the importance of ongoing injections and possible side effects is key.
- OCT imaging helps monitor disease progression and adjust dosing schedules for optimal outcomes.
- Open patient-provider communication builds trust and enhances treatment success.
About: Doctor Medica is your trusted supplier of top-quality dermal fillers, viscosupplements, and more for your medical practice. We offer genuine products from leading brands at the lowest prices. Contact Doctor Medica today to order Eylea online for your practice.
Standard Dosing Schedules for Eylea
The Eylea dosing schedule varies based on the condition being treated, and sticking to the right timeline is essential for preserving vision and slowing disease progression.
Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
- Initial Phase: 2 mg injection every 4 weeks for the first three months.
- Maintenance Phase: 2 mg injection every 8 weeks thereafter.
- Some patients may transition to 12-week intervals based on clinical response.
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) and Diabetic Retinopathy (DR)
- Initial Phase: 2 mg injection every 4 weeks for the first five injections.
- Maintenance Phase: 2 mg every 8 weeks, possibly extending intervals based on disease stability.
Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO)
- Initial Phase: 2 mg injection every 4 weeks.
- Continued monthly injections are recommended until vision is stable.
Individualized adjustments are often made based on patient outcomes, balancing clinical effectiveness with the burden of frequent visits.
Injection Techniques and Best Practices
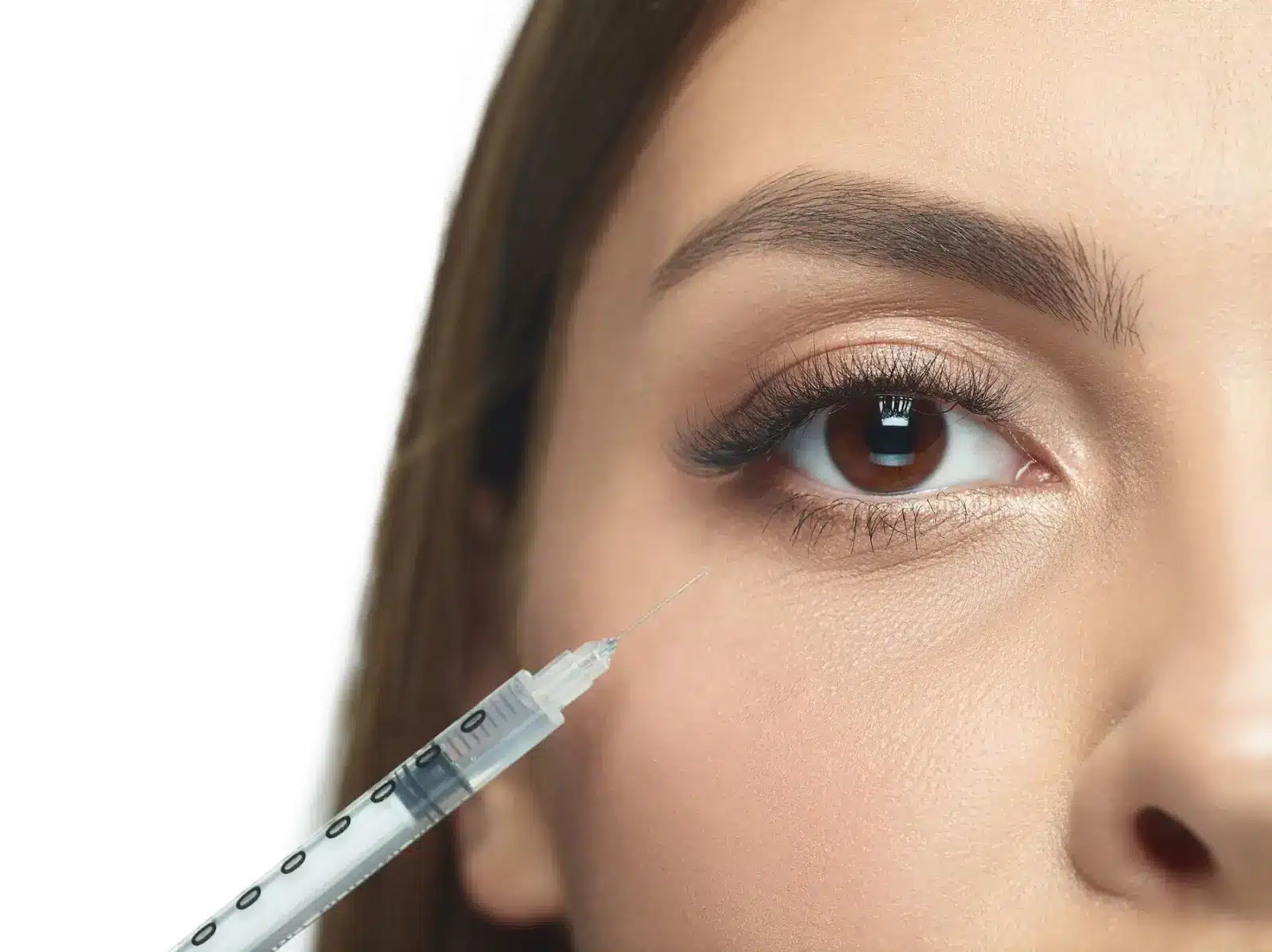
A successful Eylea treatment starts well before the needle touches the eye. Patient preparation, sterile protocols, and precise injection techniques all play a role.
Preparation begins with confirming the diagnosis, discussing treatment expectations, and applying topical anesthetic to reduce discomfort.
Sterile technique is critical. The ocular surface is disinfected with povidone-iodine to prevent complications such as endophthalmitis—a rare but serious infection.
Injection involves delivering 2 mg (0.05 mL) of Eylea into the vitreous cavity using a 30-gauge needle. The injection is placed at the pars plana, and rotating sites with each session helps prevent localized irritation.
Managing and Minimizing Injection-Related Complications
While Eylea is generally safe, it’s still important to be aware of potential side effects and how to handle them quickly.
Common Reactions
- Mild redness or irritation
- A temporary feeling of pressure or discomfort
- Floaters from tiny air bubbles
Rare but Serious Risks
- Retinal detachment
- Eye infection (endophthalmitis)
- Elevated intraocular pressure
Timely identification and intervention help mitigate risks and protect long-term vision outcomes.
Patient Adherence and Education
Ongoing success with Eylea depends heavily on patient consistency and understanding of the treatment plan.
Key Patient Education Points
- Injection Frequency: Regular injections are necessary to maintain visual improvements.
- Side Effects: Discuss both common reactions and uncommon concerns—some patients even ask, “does Eylea cause hair loss?” While not listed as a common side effect, open dialogue helps address anxieties and reinforces trust.
- Lifestyle Advice: Post-injection, patients should avoid heavy lifting and follow care instructions.
- Follow-Up: Regular check-ups are crucial for monitoring disease status and adjusting the treatment plan.
Empowered patients who understand their treatment plan are more likely to follow it consistently, leading to better long-term outcomes.
Expert Recommendations for Optimal Outcomes
Personalized dosing is key. Ophthalmologists adjust schedules based on how the retina responds—extending injection intervals when stability is achieved, or shortening them if signs of disease return.
OCT imaging (optical coherence tomography) is used regularly to assess fluid levels in the retina, offering real-time insight into disease activity and guiding treatment frequency.
Open communication between doctor and patient builds confidence. When patients feel involved in their care, they’re more likely to remain on schedule and achieve better outcomes.
Conclusion
Eylea treatment isn’t just about following a calendar—it’s a comprehensive approach that blends expert technique, ongoing monitoring, and proactive patient education.
By personalizing dosing schedules and maintaining consistent follow-up, practitioners can help patients preserve their vision and quality of life. And for patients, asking the right questions opens the door to more transparent, reassuring care.
FAQs
1. How often is Eylea administered?
It depends on the condition. Most regimens begin with monthly injections, transitioning to every 8 or 12 weeks during the maintenance phase.
2. What is the injection process like?
Eylea is injected into the vitreous cavity of the eye using a fine needle under sterile conditions with topical anesthesia for comfort.
3. What are the most common side effects?
Temporary redness, discomfort, or floaters are common and usually resolve without intervention.
4. Are there serious risks?
Rare complications include endophthalmitis, increased intraocular pressure, and retinal detachment. Patients need immediate care if these occur.
5. How can patients improve their outcomes?
By sticking to the recommended schedule, attending follow-ups, and maintaining open communication with their ophthalmologist.
References
Garweg JG, Štefanickova J, Hoyng C, et al. Dosing Regimens of Intravitreal Aflibercept for Diabetic Macular Edema Beyond the First Year: VIOLET, a Prospective Randomized Trial. Adv Ther. 2022;39:2701-2716. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12325-022-02119-z
Pieramici DJ, Awh CC, Chang M, et al. Port Delivery System With Ranibizumab vs Monitoring in Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Without Macular Edema. JAMA Ophthalmology. Published online March 6, 2025. doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2025.0001
DailyMed. EYLEA- aflibercept injection, solution. https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=f96cfd69-da34-41ee-90a9-610a4655cd1c
Related Articles
Joanna Carr
Restylane For Cheeks: Why Doctors Use Restylane For Cheeks
Interested to learn more about Why Doctors Use Restylane For Cheeks? Browse Doctor Medica's comprehensive listing of blog posts.
Joanna Carr
Couch Potatoes Age Much Faster, Research Suggests
Interested to learn more about Research Suggesting Couch Potatoes Aging Much Faster? Browse Doctor Medica's comprehensive listing of blog posts.
Joanna Carr
How Long Do HYAcorp Fillers Last? Factors Influencing Longevity
Discover the longevity of HYAcorp fillers and the factors that influence their duration. Learn how treatment areas, individual metabolism, and advance...


