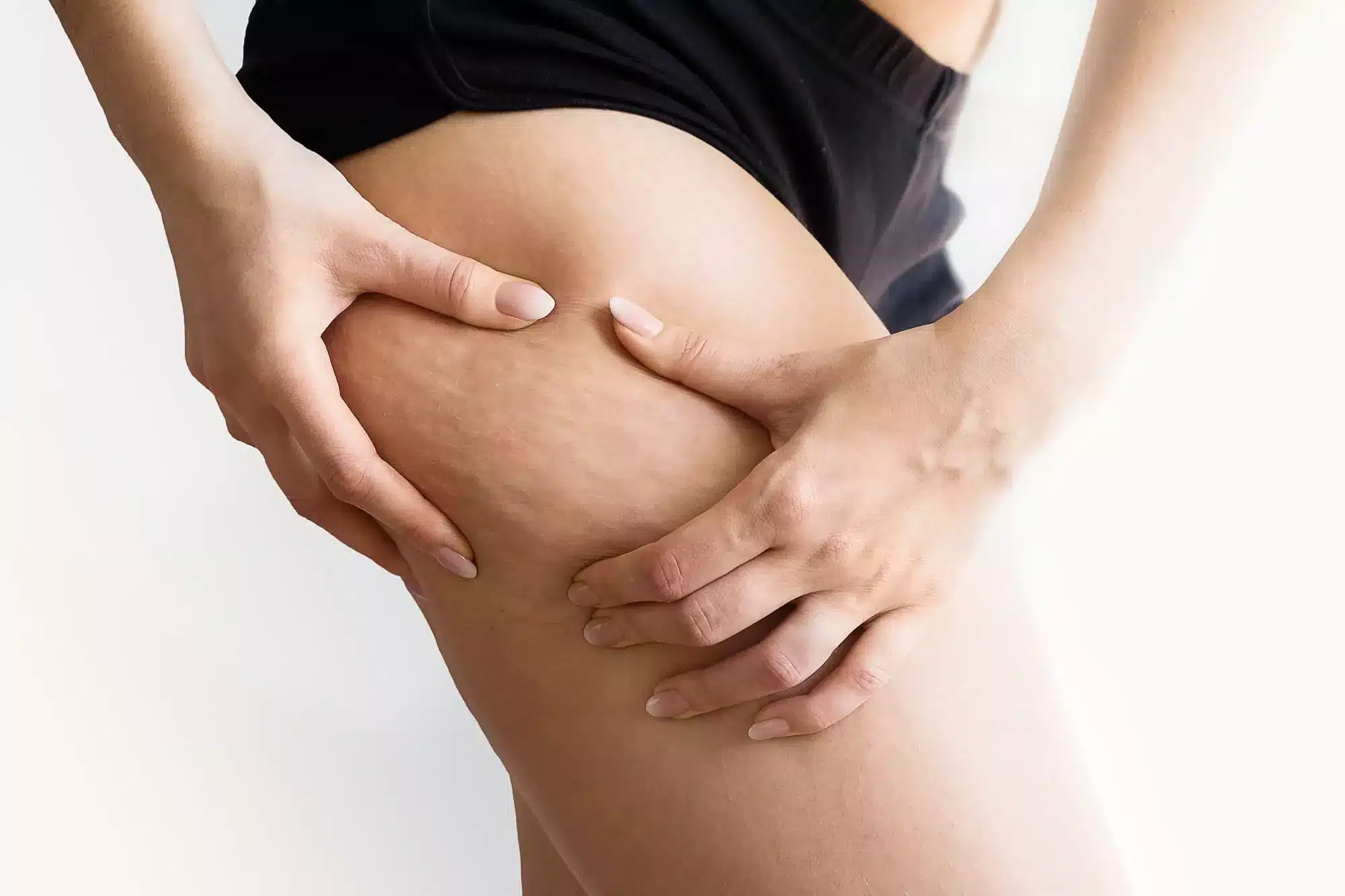
Regarding body concerns, two distinct conditions often lead to confusion: one affecting the skin texture and the other disproportionate fat distribution. We are talking about lipedema and cellulite. These conditions not only impact physical appearance but can also affect a person’s overall well-being and self-confidence. Understanding the differences between these conditions can help individuals better navigate their specific concerns.
What Is Cellulite?
Cellulite is a common cosmetic concern characterized by the dimpled or lumpy appearance of the skin, typically seen on areas like the thighs, buttocks, and abdomen. Cellulite mainly affects women and occurs when fat deposits push through the connective tissues under the skin, resulting in a dimpled appearance.
While various treatments are available to improve cellulite’s appearance, complete eradication is impossible. This is something both cellulite and lipedema have in common. The following are surgical and non-surgical ways of dealing with it:
- Exercise and weight loss
- Lotions and creams with retinol and caffeine
- Laser treatment
- Subcision
- Vacuum-assisted precise tissue release
- Carboxytherapy
- Spa treatments (endermologie and ionithermie cellulite reduction treatments)
- Radiofrequency
- Laser-assisted liposuction
- Ultrasound
It’s important to note that cellulite is not a medical condition and does not pose significant health risks.
What Is Lipedema?
Lipedema is a chronic condition involving abnormal fat cell accumulation, primarily in the lower body, such as the hips, thighs, and buttocks. It predominantly affects women and is often characterized by an asymmetrical fat distribution. Individuals with lipedema may experience disproportionate swelling, pain, tenderness, and easy bruising in the affected areas. It is a progressive condition that can worsen over time if left untreated. Unlike cellulite, lipedema can severely impact the patient’s quality of life.
Luckily, various treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life, such as:
- Exercise and an anti-inflammatory diet
- Skin moisturizers
- Supplements
- Medications
- Compression stockings
- Pneumatic compression device
- Lymphatic drainage massage
- Complex decongestive therapy
- Liposuction
Still, these measures cannot eliminate the condition entirely. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals with lipedema. The exact cause of lipedema is still unknown, but hormonal factors and genetic predisposition are believed to play a role.
Critical Differences Between Lipedima and Cellulite
While both share the common characteristic of affecting the skin’s appearance through fat deposits, they differ significantly in terms of their causes, distribution, physical symptoms, progression, and treatment options.
Cause: Lipedema is caused by the abnormal accumulation of fat cells, while cellulite primarily occurs due to the protrusion of fat deposits through the connective tissues beneath the skin. While fat is to blame in both cases, this occurs in two distinct ways.
Distribution: Lipedema typically affects the lower body, such as the hips, thighs, and buttocks, and often has an asymmetrical distribution. It can sometimes happen on the upper arms but never on the feet or hands. Conversely, cellulite can occur in various areas of the body, including the thighs, buttocks, abdomen, and arms.
Physical Symptoms: Lipedema may present with symptoms like disproportionate swelling, chronic pain, tenderness, spongy skin, and easy bruising in the affected areas. Cellulite is characterized by a dimpled or “orange peel” appearance on the skin, though this can sometimes be the case in the early stages of lipedema, too. When we compare cellulite and lipedema, note that cellulite only has cosmetic ones, whereas lipedema, especially at advanced stages, can have more serious bodily effects.
Progression: Lipedema is a progressive condition that can worsen over time if left untreated. Although it may change in appearance, cellulite does not typically progress or worsen significantly over time.
Treatment Options: While there is no 100% cure for either condition, treatment options are available. Lipedema management may involve compression therapy, an anti-inflammatory diet, specialized exercises, liposuction, a pneumatic compression device, and lymphatic drainage massages. Cellulite treatment options may include creams and lotions, massage techniques, laser-assisted liposuction, subcision, and radiofrequency treatments.
How To Differentiate Lipedema From Cellulite
Early detection and prompt initiation of effective treatment are crucial for slowing the progression of lipedema. The easiest way to do it is by physical examination.
Look at the appearance: Both conditions affect our skin through fat deposits and cause it to look uneven, but this is where most of the similarities between cellulite and lipedema end.
Cellulite typically appears as a lumpy or dimpled texture, while lipedema is characterized by disproportionate fat accumulation in the legs, buttocks, upper arms, and hips. Lipedema notably never affects the hands and feet, making this a definitive telltale sign for distinguishing between the two conditions.
Notice any pain or swelling: Cellulite on it’s own isn’t normally associated with sensations of pain or swelling, however, lipedema is known to cause these symptoms. One of the simplest ways to test for this is to pinch the area designated, to test in a way that should not cause pain. If this does produce pain, it could be early signs of lipedema. The associated pain is a key distinction between cellulite and lipedema.
The texture should not be solely relied upon for diagnosing lipedema, though. That’s because, similar to cellulite, the skin can develop an orange peel-like appearance in certain areas. By the time distinct fat lumps and pearls become evident, indicating lipedema, the condition has often progressed to an advanced stage.
Conclusion
When we compare cellulite vs. lipedema, we can see why it’s important for medical professionals to make the distinction early on. While cellulite primarily affects cosmetic appearance, lipedema is a progressive condition that can lead to significant physical symptoms and an impaired quality of life if left untreated. Fortunately, various non-surgical and surgical methods, such as Fillmed, are available that can effectively address both while significantly improving the quality of life for patients.
By understanding the critical differences, medical professionals can identify them early on and provide patients with the necessary treatments and support to minimize the impact of these conditions.
FAQ
How do I know if I have lipedema or cellulite?
Lipedema is characterized by disproportionate fat accumulation, tenderness, and pain, while cellulite primarily gives the skin an “orange peel” appearance without any tenderness or pain.
How can you tell the difference between fat legs and lipedema?
Even though it may not look good, fat accumulation does not hurt physically. If you have lipedema, your legs will be painful and sensitive to touch.
How can I tell if I have lipedema?
If you start developing larger thighs and lower legs, but your feet remain unchanged, you may have started developing lipedema. A surefire way to know will be if the area starts being sensitive to any kind of pressure.
References:
- Lipedema Can Be Treated Non-Surgically: A Report of 5 Cases; Alexandre Campos Moraes Amato and Daniel Augusto Benitti; Dec 2021
- Lipedema—Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options; Philipp Kruppa, Iakovos Georgiou, Niklas Biermann (Dr. med.), Lukas Prantl, (Prof. Dr. ,Dr. med.), Peter Klein-Weigel (Dr. med.), and Mojtaba Ghods (Dr. med.); Jun 2020
- New Insights on Lipedema: The Enigmatic Disease of the Peripheral Fat; Anna-Theresa Bauer, Dominik von Lukowicz, Katrin Lossagk, Matthias Aitzetmueller, Philipp Moog, Michael Cerny, Holger Erne, Daniel Schmauss, Dominik Duscher, Hans-Guenther Machens; Dec 2019
- Lipedema: a frequently misdiagnosed and misunderstood fatty deposition syndrome; Caroline E Fife, Erik A Maus, Marissa J Carter; Feb 2010
- Lipedema: an inherited condition; Anne H Child, Kristiana D Gordon, Pip Sharpe, Glen Brice, Pia Ostergaard, Steve Jeffery, Peter S Mortimer; Apr 2010
- Cellulite: Current Understanding and Treatment; Allen Gabriel, Vivian Chan, Marissa Caldarella, Tanya Wayne, Erin O’Rorke; Jun 2023
- Combined Monopolar Radiofrequency and Targeted Pressure Energy for the Treatment and Improvement of Cellulite Appearance on Multiple Body Parts; Mariano Busso and Trevor Born; May 2023
- Histological aspects of cellulite: shedding light on 100 years of uncertainties; M S Di Carmine, D Amuso, A Greco Lucchina, L Valbonetti, F Lorusso, and A Scarano; Apr 2023
Related Articles
Joanna Carr
Botulax vs Innotox – A Thorough Comparison of Toxin
Compare Botulax and Innotox, two leading botulinum toxin type A products from South Korea. Explore differences in formulation, preparation, onset, and...
Joanna Carr
Is A Thread Facelift Worth It? Surgical Facelift Quick Guide
Interested to learn more about Thread Facelifts, Worth It? Surgical Facelift Quick Guide? Browse Doctor Medica's comprehensive listing of blog posts.
Joanna Carr
Saxenda vs Victoza – A Thorough Comparison
Saxenda is for adults who need to lose weight. It controls how much you eat by making you feel full.


