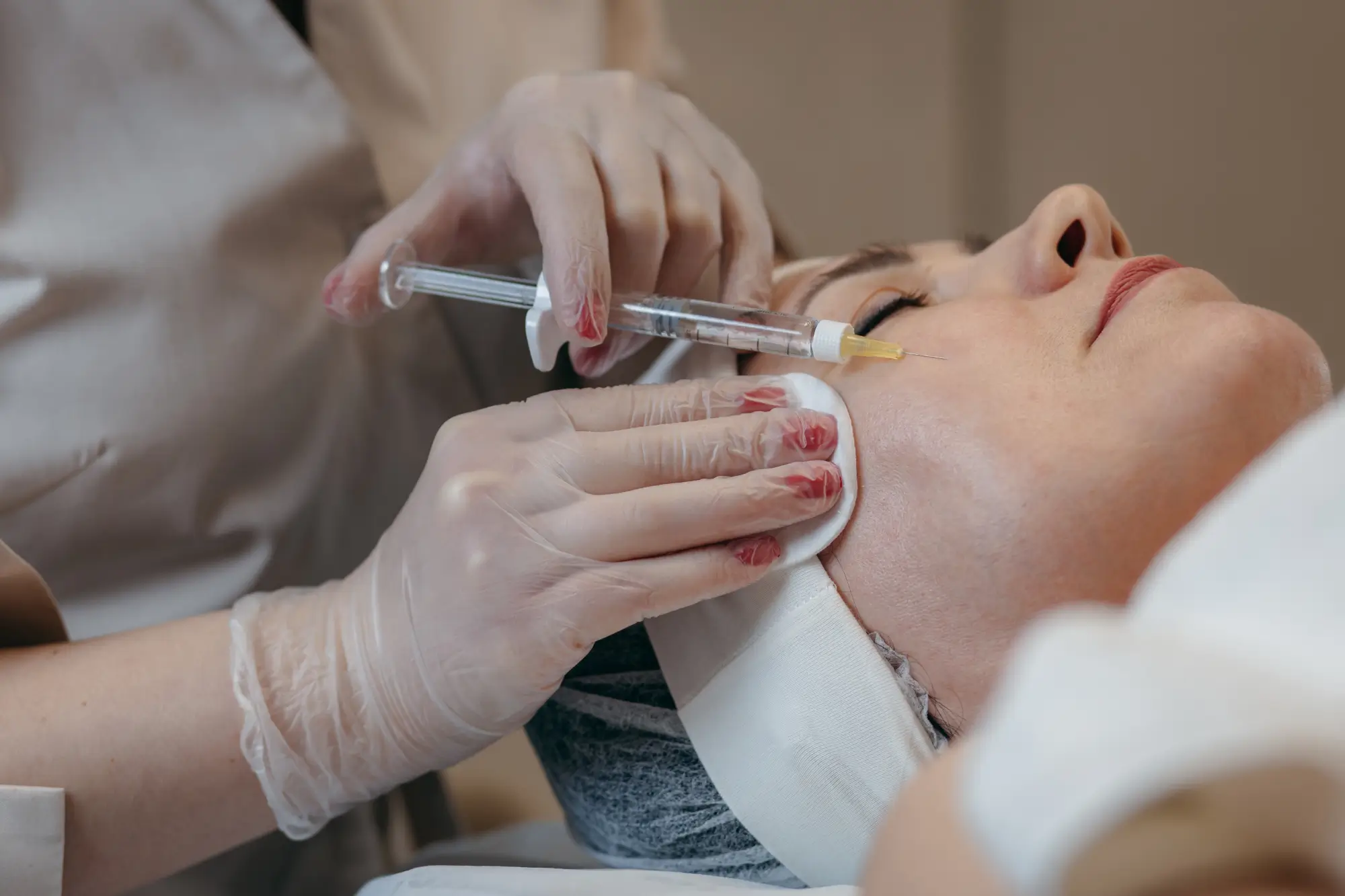
FDA approval is a critical benchmark in the cosmetic and medical fields. It ensures that products meet stringent safety and efficacy standards. For patients and practitioners alike, it builds trust and confidence in aesthetic treatments.
Neauvia fillers, celebrated for their advanced formulations and natural-looking results, have become a global favorite in the realm of aesthetic medicine. However, questions often arise about their FDA approval status, especially among patients seeking reassurance about their safety and effectiveness.
In this article, we will examine the FDA approval status of Neauvia fillers, their regulatory standing, safety profile, and implications for their use in cosmetic procedures.
Key Takeaways
- Neauvia fillers are widely accepted and approved in several international markets, highlighting their strong safety profile and effectiveness.
- They have not yet received FDA approval, primarily due to the rigorous and time-intensive process required by U.S. regulations.
- This filler uses biocompatible ingredients like hyaluronic acid, with side effects typically limited to mild, temporary issues such as swelling or redness.
- Healthcare providers must prioritize patient safety by using approved products and ensuring proper sourcing and administration of Neauvia fillers where they are authorized.
About: Doctor Medica is your trusted supplier of top-quality dermal fillers, viscosupplements, and more for your medical practice. We offer genuine products from leading brands at the lowest prices. Contact Doctor Medica today to order Neauvia online for your practice.
The Role of the FDA in Regulating Dermal Fillers

The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is a federal agency responsible for protecting public health by ensuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, and medical devices. The FDA’s regulatory authority extends to a wide range of products, including dermal fillers, which are classified as medical devices.
Importance of FDA Approval
FDA approval is crucial for medical products, including dermal fillers, as it assures that the product has been rigorously tested and meets strict safety and efficacy standards. Before a dermal filler can be marketed in the United States, the manufacturer must submit clinical data to the FDA demonstrating that the product is safe and effective for its intended use.
This process helps ensure that consumers have access to products that have been thoroughly evaluated and are manufactured to high-quality standards.
Specific Considerations for Dermal Fillers
For dermal fillers, the FDA evaluates several factors, including:
- Materials Used: The FDA assesses the safety of the materials used in the fillers, such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, or poly-L-lactic acid.
- Clinical Testing: The FDA reviews clinical studies that examine the product’s performance, side effects, and potential complications.
- Labeling and Instructions: The FDA ensures that the product labeling includes clear instructions for use and warnings about potential risks.
- Manufacturing Practices: The FDA inspects manufacturing facilities to ensure that the products are produced in compliance with good manufacturing practices (GMP).
Neauvia Fillers
Neauvia fillers, known for their use of hyaluronic acid and other components, have gained significant popularity in the field of medical aesthetics. However, Neauvia fillers themselves are not FDA-approved in the United States. Despite this, their primary component, hyaluronic acid, is FDA-approved for safety. Additionally, some of Neauvia’s devices, such as Plasma IQ and Laser ME, have received FDA approval.
Globally, Neauvia fillers have achieved CE marking under the European Union’s new Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which is a more stringent certification process compared to its predecessor. This certification underscores the company’s commitment to clinical safety and transparency.
The variations in approval status across different countries mean that medical professionals must stay informed about the regulatory landscape in their respective regions. For patients, it highlights the importance of consulting with certified practitioners who use approved products to ensure safety and efficacy.
Challenges and Ongoing Discussions Regarding Neauvia’s FDA Approval
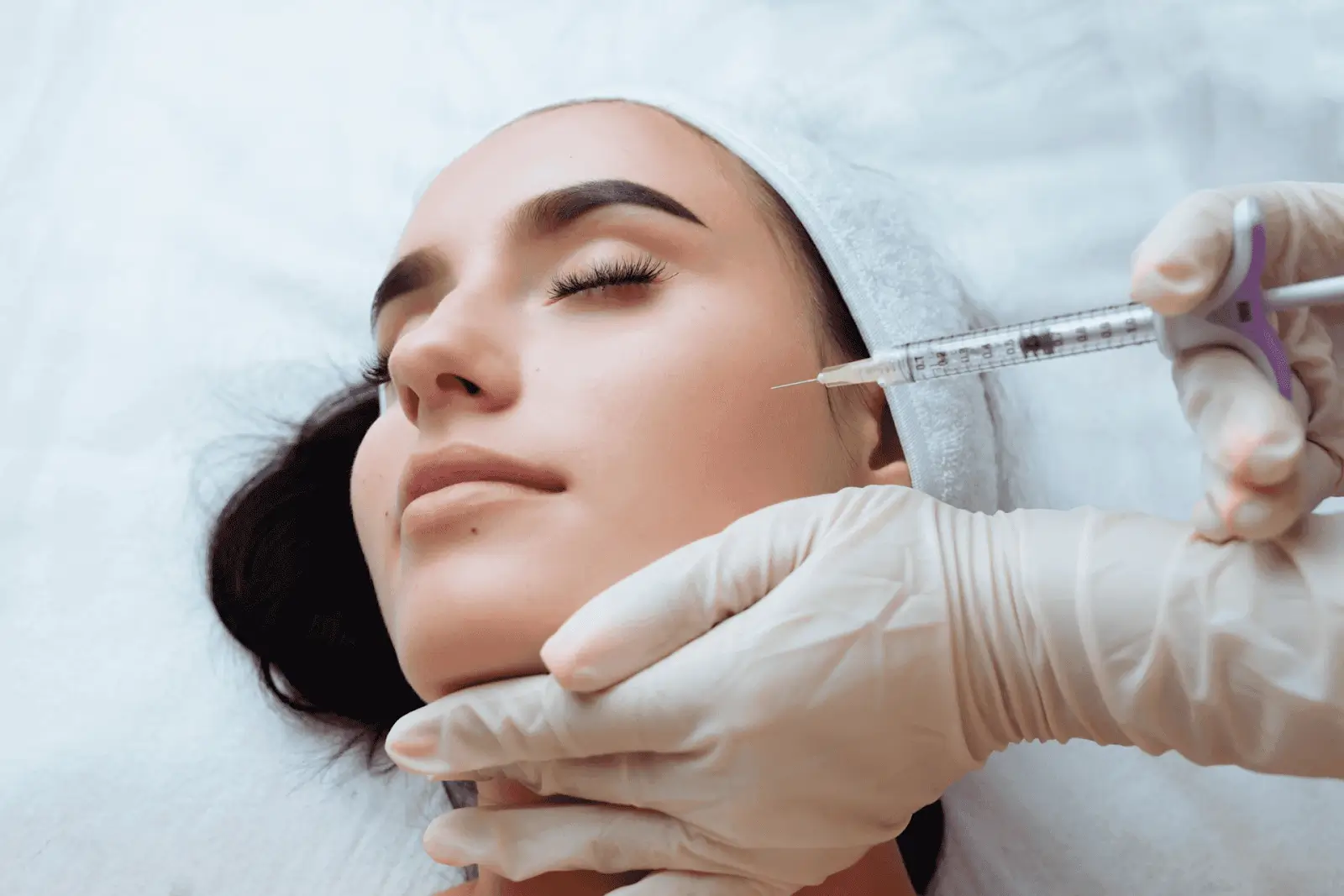
One of the primary factors influencing the approval process is the rigorous evidence required to demonstrate safety and efficacy. The FDA demands comprehensive clinical trial data, which can be time-consuming and costly for manufacturers. Additionally, the evolving regulatory landscape and the need for compliance with stringent guidelines add layers of complexity to the approval process.
The potential impact on medical practice and patient care is significant. Without FDA approval, medical professionals may be hesitant to use Neauvia fillers, limiting treatment options for patients. This can also affect the credibility and marketability of the product, as patients and practitioners alike look at FDA approval as a benchmark for safety and effectiveness.
The lack of FDA approval may raise concerns about the treatment’s reliability and safety, influencing patients’ decision-making process.
Safety Profile and Considerations for Medical Professionals
Neauvia fillers, while not FDA-approved, are formulated with biocompatible ingredients such as hyaluronic acid and PEGDE (polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether), which contribute to their high safety profile.
Common Neauvia filler side effects include temporary swelling, redness, bruising, and tenderness, which typically resolve within a few days. Serious complications like infections, allergic reactions, or vascular occlusions are rare but require prompt medical attention.
Medical professionals considering offering Neauvia fillers should conduct thorough patient assessments to identify any contraindications, such as allergies to PEGs or certain autoimmune disorders. Proper injection techniques and adherence to post-treatment care instructions are crucial to minimize risks and achieve natural-looking results.
Compared to FDA-approved dermal fillers like Juvederm, Neauvia fillers utilize a unique Smart Crosslinking Technology that enhances their safety and integration into the skin. However, the lack of FDA approval means that practitioners must rely on clinical studies and international regulatory approvals to ensure patient safety.
Conclusion
Neauvia fillers have established a solid reputation globally for their innovative formulations and natural results. However, the absence of FDA approval in the U.S. underscores the complexities of regulatory pathways and the varying standards across countries.
For medical professionals, understanding Neauvia’s global safety profile and regulatory status is essential for informed practice. Patients should consult certified practitioners to ensure safe and effective treatment, fostering trust and confidence in their aesthetic procedures.
FAQs
1. Can U.S. medical professionals use Neauvia fillers?
Without FDA approval, doctors based in the United States cannot use them. Medical professionals must rely on FDA-approved alternatives until regulatory status changes.
2. Are Neauvia fillers safe without FDA approval?
While not FDA-approved, Neauvia fillers have been tested and approved in many other regions, meeting strict international safety standards. Moreover, hyaluronic acid products that deliver similar results to Neauvia fillers also have FDA approval.
3. What are common Neauvia filler side effects?
Typical side effects include swelling, redness, tenderness, and bruising at the injection site, which usually resolve within a few days. Rare but serious complications include infections or vascular occlusions.
References
Nass SJ, Levit LA, Gostin LO. The value, importance, and oversight of health research. Beyond the HIPAA Privacy Rule – NCBI Bookshelf. Published 2009. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9571/
Dhruva SS, Darrow JJ, Kesselheim AS, Redberg RF. Experts’ views on FDA Regulatory Standards for Drug and High-Risk Medical Devices: Implications for Patient care. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2022;37(16):4176-4182. doi:10.1007/s11606-021-07316-0
Lee, J. H., Kim, J., Lee, Y. N., Choi, S., Lee, Y. I., Suk, J., & Lee, J. H. (2024). The efficacy of intradermal hyaluronic acid filler as a skin quality booster: A prospective, single‐center, single‐arm pilot study. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 23(2), 409-416.
Related Articles
Joanna Carr
Cimzia Indications – FDA-Approved Uses and Conditions Treated by Cimzia
Discover the FDA-approved uses and conditions treated by Cimzia. Learn about its indications for rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, psoriatic arth...
Joanna Carr
Wegovy and Depression – Is There a Connection?
Existing research suggests a potential link between Wegovy and depressive symptoms, although further investigation is needed.
Joanna Carr
How Many People Get Botox? 10+ Botox Statistics For 2023
Have an interest in learning about How Many People Get Botox, and 10+ Botox Statistics For This Year? Browse Doctor Medica's extensive archive of blog...


