
Vitamin D is vital in maintaining bone health, yet a significant portion of the global population remains deficient. According to a recent review, about 40% of Europeans and nearly one billion people worldwide have insufficient vitamin D levels. This widespread deficiency contributes to weakened bones and a higher risk of osteoporosis, highlighting the urgent need for treatments that go beyond supplementation alone.
Among the therapies designed to manage bone loss, Prolia and Reclast are two widely used options. Both treatments aim to strengthen bones and reduce fracture risk, but they work through different mechanisms and follow different dosing schedules, which can significantly influence clinical outcomes and patient preferences.
In this article, we’ll directly compare Prolia vs Reclast, explaining their key differences, benefits, and critical considerations to help healthcare providers and patients make more informed, confident treatment decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Prolia and Reclast are both effective treatments for osteoporosis. They work through different mechanisms: Prolia inhibits osteoclast formation via RANKL blockade, while Reclast disables active osteoclasts by binding to bone.
- The standard dosage for Prolia is 60 mg administered subcutaneously every six months, whereas Reclast is a 5 mg intravenous infusion given once yearly.
- Prolia is often preferred for patients with chronic kidney disease, those who need a reversible therapy, or patients who benefit from semi-annual dosing.
- Patients who prefer once-a-year administration, require longer residual protection, or have cost concerns may favor Reclast.
- Both medications are effective at increasing bone mineral density and reducing fracture risk, but their side effect profiles differ. Prolia is more associated with hypocalcemia, while Reclast commonly causes flu-like symptoms post-infusion.
- Regular monitoring of calcium, vitamin D, and kidney function is essential for both treatments to reduce the risk of complications like osteonecrosis of the jaw or atypical femoral fractures.
- Choosing between Prolia and Reclast should be based on a combination of patient medical history, treatment goals, and lifestyle preferences, with healthcare providers guiding individualized treatment decisions.
About: Doctor Medica is your trusted supplier of top-quality dermal fillers, viscosupplements, and more for your medical practice. We offer genuine products from leading brands at the lowest prices. Contact Doctor Medica today to order Prolia online for your practice.
Mechanisms of Action: Prolia vs Reclast
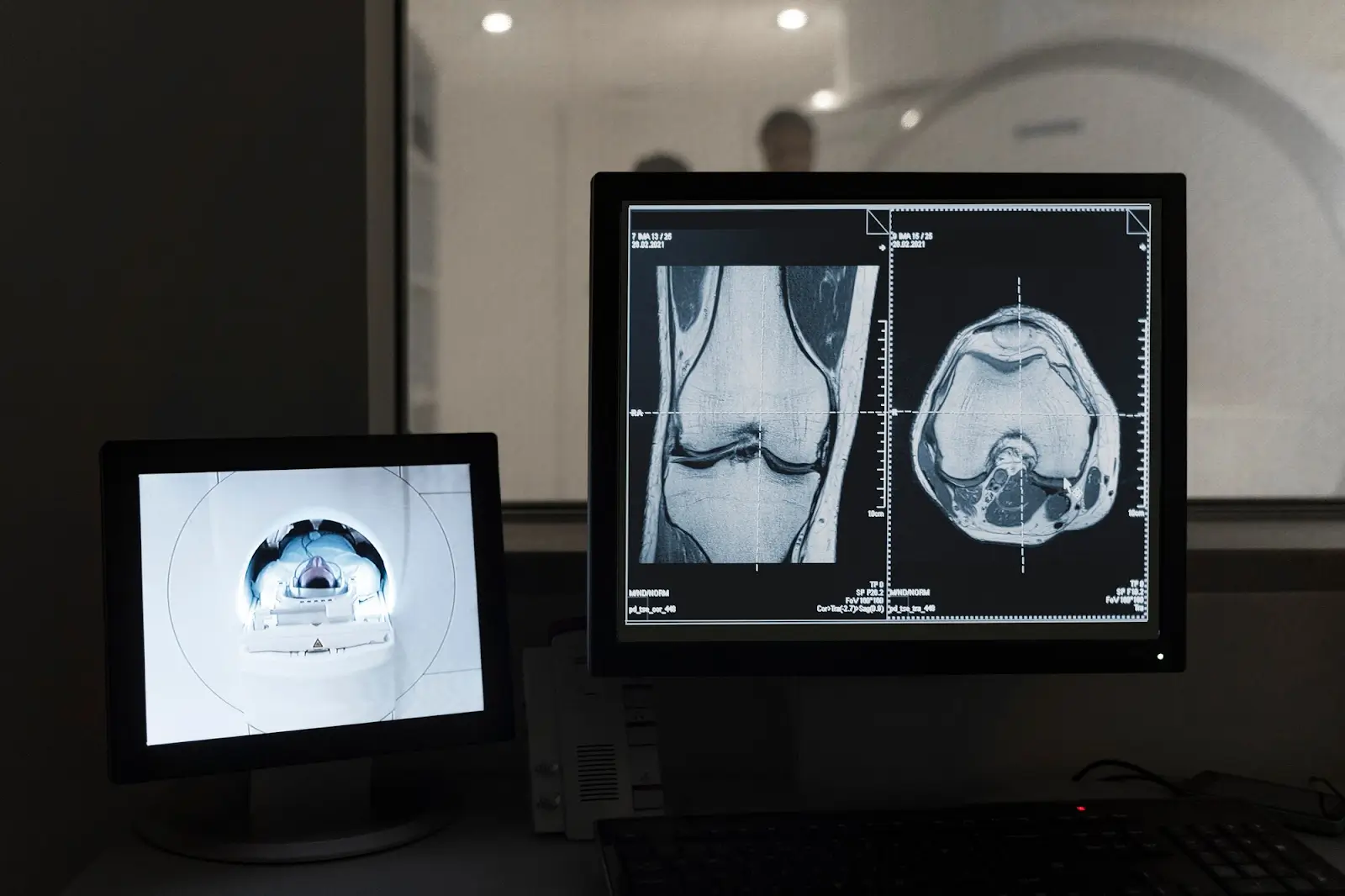
Understanding how each medication works is key to comparing them effectively. Prolia (denosumab) is a monoclonal antibody that targets and binds to RANK ligand (RANKL), a key regulator of osteoclast formation.
By blocking RANKL, Prolia prevents the development and activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption. This inhibition significantly slows bone loss and helps preserve bone density, making Prolia highly effective in reducing fracture risk, particularly in patients with osteoporosis.
Reclast (zoledronic acid), in contrast, is a bisphosphonate administered intravenously. It binds directly to the bone mineral matrix and interferes with osteoclast-mediated pathways, leading to the inactivation of existing osteoclasts.
Simply put, Prolia prevents osteoclasts from forming, while Reclast disables those already active, resulting in improved skeletal strength via different biological mechanisms.
These differences impact treatment choice and how quickly effects are seen, how long they last, and how easily they can be reversed if needed.
Administration and Dosing Schedules
A major distinction between Prolia vs Reclast lies in their administration route and frequency, both of which can significantly influence patient preference and adherence.
Prolia is administered as a subcutaneous injection every six months, typically in a clinical setting. The standard Prolia dosage is 60 mg, delivered by a healthcare provider following baseline lab checks. This twice-yearly schedule offers convenience and flexibility, especially for patients who prefer less frequent but still active involvement in their care.
Reclast, on the other hand, is given via intravenous infusion once a year, with the infusion lasting at least 15 minutes. A single 5 mg dose provides sustained antiresorptive effects, which may appeal to patients seeking a more hands-off approach.
Both treatments require patient observation during and after administration to monitor for immediate side effects such as allergic reactions or infusion-related symptoms. Educating patients about each medication’s schedule and tolerability helps guide treatment selection based on lifestyle and clinical needs.
Efficacy and Safety Profiles Comparison
Both Prolia and Reclast have shown strong efficacy in increasing bone mineral density (BMD) and reducing fracture risk. However, their side effect profiles, onset of action, and long-term tolerability differ in ways that may be important for treatment planning.
| Aspect | Prolia | Reclast |
| Effect on BMD | Increases BMD at the spine, hip, and femur | Improves BMD, especially at the spine |
| Fracture Risk Reduction | Reduces vertebral, non-vertebral, and hip fractures | Reduces fracture risk, particularly vertebral fractures |
| Common Side Effects | Joint pain, back pain, hypocalcemia, infections | Fever, muscle aches, and flu-like symptoms after infusion |
| Rare Risks | Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), atypical femur fractures | ONJ, kidney impairment, atypical femur fractures |
| Monitoring Needed | Baseline checks for calcium, kidney function, and vitamin D levels | Baseline checks for calcium, kidney function, and vitamin D levels |
Both therapies require baseline evaluations and routine follow-up testing to detect early signs of rare adverse effects and to guide safe continuation of therapy.
Patient Suitability for Prolia vs Reclast

When evaluating Prolia vs Reclast, healthcare providers must consider individual patient characteristics, including comorbidities, lifestyle preferences, renal function, and adherence potential.
Prolia may be preferred when:
- The patient has chronic kidney disease, as it is not renally cleared, making it safer in those with impaired kidney function.
- Adherence is a concern, and the patient may benefit from the simplicity of semi-annual injections.
- A reversible treatment is preferred. Since Prolia’s effects wear off within months of discontinuation, it may be better suited for patients needing flexible plans.
Reclast may be preferred when:
- The patient prefers a once-a-year dosing schedule and minimal office visits.
- A longer-lasting residual effect post-treatment is beneficial (as seen in many bisphosphonates).
- Cost is a major factor, as Reclast is often more affordable than biologics.
Regardless of choice, ongoing patient monitoring, clear communication, and periodic reassessment are critical to ensure treatment remains effective and well-tolerated.
Conclusion
When comparing Prolia vs Reclast, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Each medication offers distinct benefits and comes with unique considerations based on the patient’s medical history, bone density goals, and lifestyle factors.
Prolia delivers targeted inhibition of bone resorption with semi-annual dosing and reversibility, while Reclast provides once-yearly IV administration with lasting protection and affordability. Clinicians must evaluate efficacy, safety, and patient preference to make the most appropriate and personalized choice for long-term osteoporosis management.
FAQs
1. Which works faster, Prolia or Reclast?
Both effectively improve bone density, but Prolia often shows slightly faster BMD gains within the first 6–12 months.
2. Is Prolia safer for patients with kidney problems?
Yes, Prolia can be used cautiously in patients with kidney issues since it is not cleared renally like Reclast.
3. Can I switch from Reclast to Prolia or vice versa?
Switching is possible but requires careful coordination with your healthcare provider to prevent gaps in bone protection.
4. What supplements should I take with Prolia or Reclast?
Both treatments require patients to maintain adequate calcium and vitamin D intake to minimize the risk of hypocalcemia and maximize treatment efficacy.
5. How are Prolia and Reclast administered?
Prolia is given as a subcutaneous injection every six months, while Reclast is administered as an intravenous infusion once yearly.
6. What are the common side effects of Prolia and Reclast?
Prolia’s common side effects include joint pain, back pain, and infections. Reclast often causes flu-like symptoms, fever, and muscle aches after infusion.
7. Can Prolia or Reclast cause serious side effects?
Both carry rare risks such as osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) and atypical femur fractures. Reclast may also affect kidney function, so monitoring is essential.
8. How long do the effects of Prolia and Reclast last after stopping treatment?
Prolia’s effects diminish relatively quickly after discontinuation, potentially increasing fracture risk if not followed by another therapy. Reclast has a longer residual effect due to bisphosphonate bone binding.
9. Who should avoid Prolia or Reclast?
Patients with hypocalcemia should correct it before starting either treatment. Reclast is contraindicated in severe kidney impairment. Prolia should be used cautiously in patients with infections or immune system issues.
References
Cui A, Zhang T, Xiao P, Fan Z, Wang H, Zhuang Y. Global and regional prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in population-based studies from 2000 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 7.9 million participants. Front Nutr. 2023;10. Published March 17, 2023. doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1070808
Amrein K, Scherkl M, Hoffmann M, et al. Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2020;74(11):1498-1513. doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0558-y
Spiro A, Buttriss JL. Vitamin D: An overview of vitamin D status and intake in Europe. Nutr Bull. 2014;39(4):322-350. doi:10.1111/nbu.12108
What’s the difference between Prolia and Reclast? Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/medical-answers/difference-between-prolia-reclast-3568636/
Related Articles
Joanna Carr
Lip Augmentation Part Two: Best Fillers For Lip Augmentation
Interested in learning more about Which Are The Best Fillers For Lip Augmentation? Browse Doctor Medica's comprehensive archive of blog posts.
Joanna Carr
Depo Provera And Periods – Do They Stop Completely?
Depo Provera can significantly alter menstrual cycles, often leading to reduced bleeding or complete cessation of periods in some women.
Joanna Carr
Botox For Hyperhidrosis – An Excellent Non Surgical Alternative
Have an interest in learning about Botox For Hyperhidrosis, An Excellent Non Surgical Alternative? Browse Doctor Medica's extensive archive of blog po...


