Proper injection technique is essential for ensuring both medication effectiveness and patient safety. According to the World Health Organization, correct injection practices not only reduce complications but also improve overall treatment outcomes. This is especially critical for medications given via the subcutaneous route, where precision in dose delivery and site selection can make a meaningful difference.
Prolia, a prescription medication for treating osteoporosis, is administered as a subcutaneous injection every six months. While the process may seem simple, both patients and healthcare providers must follow specific preparation and administration protocols to ensure safe and effective delivery.
This article offers a quick and practical guide to Prolia injection administration, highlighting key steps, best practices, and what to expect before, during, and after the injection.
Key Takeaways
- Proper preparation is essential for Prolia administration: the pre-filled syringe should be stored refrigerated, allowed to reach room temperature naturally, and inspected for clarity before use.
- Prolia is administered as a 60 mg subcutaneous injection every six months, typically in the upper arm, thigh, or abdomen, using a 45–90 degree angle depending on the site.
- Post-injection care involves monitoring for 15–30 minutes, encouraging hydration, and reinforcing daily calcium and vitamin D supplementation to prevent hypocalcemia.
- Common injection-related side effects include redness, swelling, joint or muscle pain, and mild fatigue; serious risks, though rare, may include hypocalcemia, infections, or osteonecrosis of the jaw.
- Patients and providers should be aware of alternative treatment options like Prolia vs Reclast, especially when evaluating long-term care plans or risk profiles.
- Following best practices in injection technique, storage, and patient education ensures the safe, effective, and consistent delivery of Prolia for osteoporosis treatment.
About: Doctor Medica is your trusted supplier of top-quality dermal fillers, viscosupplements, and more for your medical practice. We offer genuine products from leading brands at the lowest prices. Contact Doctor Medica today if you want to order Prolia online for your practice.
Preparation for Prolia Injection
Proper preparation is essential for minimizing complications and ensuring a smooth and effective Prolia injection process. Following standard guidelines helps maintain medication integrity and patient safety.
Key preparation steps include:
- Storage: Keep Prolia refrigerated at 2°C–8°C (36°F–46°F). Do not freeze. Always protect from light and avoid temperature fluctuations during handling.
- Pre-Injection Warming: Remove the pre-filled syringe from the refrigerator and allow it to reach room temperature naturally (15–30 minutes) before use. Do not use external heat sources.
- Inspection: Visually inspect the solution through the syringe. It should be clear and colorless without visible particles. Discard if the solution appears cloudy or discolored.
- Patient Screening: Review the patient’s baseline calcium levels and confirm there are no active infections or contraindications prior to administration.
These steps set the foundation for a successful injection and reduce the risk of preventable errors.
Prolia Injection Procedure Steps
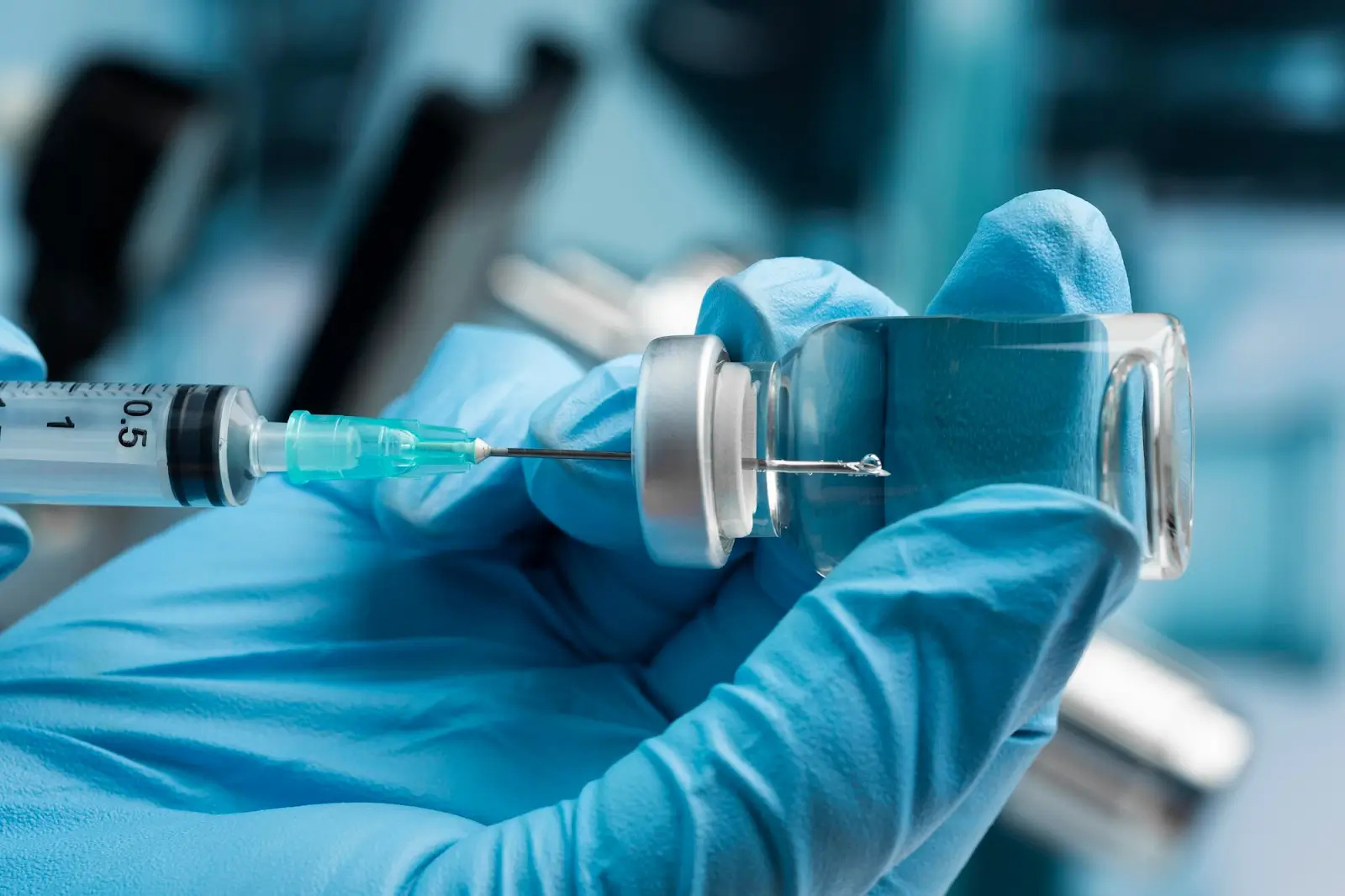
Administering Prolia requires careful attention to detail. By adhering to proper injection technique, healthcare professionals can minimize discomfort, reduce local reactions, and help ensure the medication performs as intended.
Step-by-Step Injection Guide
- Select Injection Site: Common subcutaneous sites include the upper arm, anterior thigh, or abdomen—areas with sufficient fatty tissue and easy accessibility.
- Clean the Area: Use an alcohol swab to disinfect the skin. Let the area dry before injecting to avoid stinging.
- Injection Technique: Administer the 60 mg dose using the pre-filled syringe provided. Do not shake the syringe before use.
- Injection Angle: Insert the needle at a 45 to 90-degree angle, depending on the site and needle length. Pinch the skin if needed to ensure proper subcutaneous delivery.
- Disposal: Immediately dispose of the used syringe in a designated sharps container, following facility safety protocols.
Using the correct technique improves absorption, minimizes pain, and reduces injection site complications.
Post-Injection Care and Monitoring
Post-injection monitoring is a key aspect of Prolia administration, ensuring prompt response to potential reactions and patient reassurance.
Key post-injection considerations include:
- Observation: Monitor the patient for at least 15–30 minutes to detect early signs of hypersensitivity or allergic reactions, especially in first-time users.
- Hydration: Encourage patients to maintain adequate hydration, which supports overall wellness and helps mitigate minor side effects.
- Activity: Unless otherwise directed, most patients can resume normal activities immediately following the injection, including walking and light movement.
- Supplementation: Reinforce the ongoing importance of daily calcium (1,000 mg) and vitamin D (400–800 IU) to support Prolia’s action and reduce the risk of hypocalcemia.
These measures help complete the care cycle around the injection and improve patient outcomes.
Managing Injection-Related Adverse Events
Although Prolia is generally well-tolerated, patients may experience injection-related side effects, which are typically mild and transient.
Common side effects include:
- Redness, swelling, or tenderness at the injection site
- Fatigue, joint pain, or muscle soreness
- Low calcium levels (hypocalcemia), especially in patients with kidney impairment or insufficient supplementation
In rare cases, patients may experience:
- Severe infections
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ)
- Atypical femoral fractures
If any symptoms persist or worsen, patients should seek medical evaluation promptly. It is also helpful to discuss how Prolia compares to other osteoporosis therapies—such as Prolia vs Reclast—to ensure patients understand their options and risks, especially if they have concerns about infusion reactions or long-term bone health strategy.
Open communication and proactive side effect management help preserve patient confidence and adherence.
Conclusion
Mastering the Prolia injection administration process is crucial for delivering safe and effective osteoporosis treatment. Every step—from storage and warming to injection technique and post-care monitoring—contributes to positive outcomes and improved patient experiences.
By following established protocols, healthcare professionals can reduce the risk of complications and maximize therapeutic benefit. As part of a broader osteoporosis management strategy, Prolia serves as a valuable option—especially when care teams ensure every injection is handled with precision and care.
FAQs
1. Where should Prolia be injected?
Prolia should be administered subcutaneously into the upper arm, thigh, or abdomen.
2. Can patients inject Prolia themselves?
No. A trained healthcare professional must administer Prolia to ensure proper technique and safety monitoring.
3. What should be monitored after Prolia injection?
Patients should be monitored for signs of allergic reactions and have regular calcium and vitamin D levels checked throughout therapy.
4. How does Prolia administration compare to Reclast?
While Prolia is a subcutaneous injection every six months, Reclast is an annual intravenous infusion.
5. What should I do if I miss a dose of Prolia?
If you miss a dose, get the injection as soon as possible and schedule the next dose 6 months from the date of the last injection.
6. How should Prolia be stored?
Store Prolia in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) in the original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze.
7. What does Prolia look like?
Prolia is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution. Do not use it if it is discolored, cloudy, or contains particles.
8. What should I do if I have a latex allergy?
The grey needle cap on the Prolia prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex), so people sensitive to latex should not handle the needle cap.
9. Are there instructions for self-injection in the leaflet?
The leaflet has instructions on injecting Prolia when supplied in a pre-filled syringe; your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist will show you or your carer how to use Prolia. Do not use Prolia unless proper training has been given.
References
Injection safety. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/teams/integrated-health-services/infection-prevention-control/injection-safety
Hutin Y, Hauri A, Chiarello L, et al. Best infection control practices for intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular needle injections. Published 2003. https://www.scielosp.org/article/bwho/2003.v81n7/491-500/
Related Articles
Joanna Carr
Cingal Hyaluronic Acid – About the Key Ingredient
Cingal injections mix hyaluronic acid with a steroid to ease inflammation and improve joint movement. Read more on Doctor Medica.
Joanna Carr
Botox for TMJ: An Innovative Approach to Pain Relief
Interested to learn more about Botox for TMJ, An Innovative Approach to Pain Relief? Browse Doctor Medica's comprehensive listing of blog posts.
Joanna Carr
Side Effects of Prolia – A Complete List
Prolia is effective for osteoporosis, but it comes with potential side effects. Review the most common and rare adverse reactions to make informed tre...


